Marketplace Open Enrollment
Last Updated: October 2023
Download PDF
Through the Affordable Care Act, the Health Insurance Marketplace® open enrollment is a period of time each year when you can sign up for health insurance or change your plan.
To learn more about your options, see below:
Open Enrollment FAQ
Marketplace open enrollment for health coverage is a period each year when individuals who are 19 to 64 years old — who are not eligible for Medicare, Medicaid, and are without employer-sponsored health insurance— can sign up for a health plan or make changes to the health plan which they’re already enrolled in, through the Health Insurance Marketplace® or “exchange.” This year, the open enrollment period runs from November 1, 2023 to January 15, 2024 (for most states) through the Affordable Care Act. States with their own individual marketplace and deadlines are listed below.
There are many factors to consider when selecting health insurance.
1. Decide how you will obtain health insurance.
There are a few options for getting health coverage:
- Your employer.
- Federal marketplace or exchange (healthcare.gov).
- Your specific state’s marketplace or exchange.
- A private exchange or directly from a private insurer.
2. Determine which type of plan is best for you.
After deciding how you will obtain health insurance, determine which type of plan is the best fit for you. There are three main types of health plans- Health Maintenance Organization (HMO),Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO), and Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)- each with different benefits. To compare these different plan types, consider the factors outlined in the chart below. Ask yourself which of these factors is most important to you, and then use the chart to determine which plan best fits your needs.
|
|
HMO
Health Maintenance Organization
|
EPO
Exclusive Provider Organization |
PPO
Preferred Provider Organization
|
| Does the plan require you to select a designated Primary Care Physician? |
Yes |
Sometimes |
No |
| Does the plan require you to get a referral if you want/need to see a Specialist?
|
Yes |
No |
No |
| Does the plan cover health expenses from doctors, hospitals or providers within the Provider Directory? |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| Does the plan cover health expenses from doctors, hospitals or providers outside of the plan’s network? |
No |
No |
Yes |
| How expensive will your monthly payments be? |
$ |
$$ |
$$$$ |
| Can you use a Health Savings Account to set aside pre-tax money to pay for costs not covered by your plan? |
Sometimes |
Sometimes |
Sometimes |
| Does the plan have very high out-of-pocket costs for health expenses, but very low regular monthly payments? |
Sometimes |
Sometimes |
No |
3. Compare Plans.
Plans are presented into four tiers: bronze, silver, gold & platinum. Consider the following factors when deciding what type of plan to select:
See below to determine which tier is right for you:
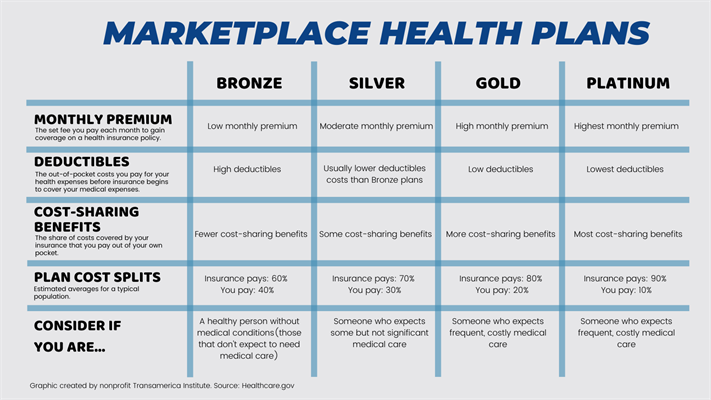
4. Determine your monthly cost.
Premiums are the monthly costs you pay for your health insurance, and deductibles are the out-of-pocket costs you must pay for your health expenses before insurance begins to cover your medical expenses. Typically, paying higher monthly premiums allows for lower deductibles, and paying lower monthly premiums allows for higher deductibles.
To decide if you want a high premium/low deductible plan or a low premium/high deductible plan, consider how often you will be using health services. A plan with a higher premium which covers a higher portion of your medical costs may be appropriate if:
-
You are expecting a baby or plan to have a baby.
-
You have a surgery coming up.
-
You need emergency care frequently.
-
You’ve been diagnosed with a chronic condition.
Options for managing out-of-pocket costs:
If you are considering a “High Deductible Health Plan” that has potentially lower monthly costs (also known as "premiums") and very high out-of-pocket costs, determine what options the plan allows for managing the out-of-pocket costs you may incur. Some High Deductible Health Plans allow you to use the following alternative sources to help pay for your out-of-pocket payments.
-
Health Savings Account (HSA): a type of savings account that allows you to set aside pre-tax money to pay for certain eligible medical expenses not covered by insurance.
-
Health Reimbursement Arrangement (HRA): an arrangement which reimburses employees tax-free for certain eligible medical expenses, funded by their employer.
Health Insurance Requirement
Federal law no longer requires individuals to purchase health insurance, however, the following states have an individual mandate as of 2023:
-
Massachusetts
-
New Jersey
-
California
-
Rhode Island
-
District of Columbia
-
Vermont
Individuals who live outside of these states who do not purchase health coverage for the year of 2024 will not have to pay a fine.
Qualifying Health Coverage
For people who are unable to afford traditional health insurance, below are some available options. Please note that if you are concerned about your ability to afford health insurance, it is best to seek advice and assistance from a professional. Many states have Navigators to answer your questions and can walk you through this process. The "Find Local Help" link on healthcare.gov or your state’s Marketplace website can get you in touch with one of these individuals.
Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP):
If your income is low, you may qualify for health coverage through a state agency. Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program provide free or low-cost coverage to millions of Americans based on need. You can apply for Medicaid or CHIP through either the Health Insurance Marketplace or your state’s Medicaid agency.
Catastrophic Coverage:
Catastrophic health plans are a low-cost option you can buy through the Health Insurance Marketplace. To meet eligibility requirements for catastrophic coverage, you must be under 30 years old or qualify for a hardship exemption due to your inability to afford all other insurance options. These plans cover the same services as other medical insurers with relatively low monthly premiums, but very high deductibles.
Short Term Health Insurance:
Short term health insurance is available outside of the marketplace, and you do not have to meet any income standards to qualify. These plans have low monthly premiums, however they are set for a designated length of time and provide a limited set of benefits. These plans are not Qualifying Health Coverage and do not meet Affordable Care Act requirements.
Supplemental Products:
Supplemental products are add-ons to other limited plans you might have, such as a Short Term Health Insurance plan. These supplemental products can help expand your coverage and build a safety net to avoid financial trouble. Some people might even use supplemental products on their own if they cannot afford health insurance. Examples of supplementary products are insurance plans specifically for dental, vision, accidents, hospitalization, or critical illness.
Advanced Premium Tax Credit:
If you are struggling to afford traditional health insurance, an Advanced Premium Tax Credit (APTC) can help you lower you monthly health insurance premiums. When you apply for coverage through the Health Insurance Marketplace, you provide an estimated expected income for the year. If this estimate allows you to qualify for a premium tax credit, you can apply the credit to lower your premium payments.
Certain life events, like losing health coverage, getting married, having a baby, or moving, may qualify you to enroll in or change Marketplace health plans outside of the annual Open Enrollment Period, which starts November 1.
Changes in Household
If any of these happened to you or someone in your household in the last 60 days, you may qualify for a Special Enrollment Period:
- Got married
- Had a baby, adopted, placed a foster child
- Lost health coverage when you got divorced or legally separated
- If someone on your health plan dies and you lose eligibility with your current plan
Changes in Residence
Changes in residence that may qualify you for a Special Enrollment Period:
- Moving to a different ZIP code or county
- Moving to the US from another country or territory
- Moving to and from the place you attend school
- Moving to or from the place you work
- Moving to or from transitional housing or a shelter
Loss of Health Insurance
You may qualify for a Special Enrollment Period if you or anyone in your household lost health coverage in the last 60 days (or since January 1, 2020) or expects to lose coverage in the next 60 days.
Coverage Losses that may qualify you for a Special Enrollment Period:
- Losing job-based coverage
- Losing individual health coverage
- Losing eligibility for Medicare
- Losing eligibility for CHIP or Medicaid
- Losing coverage through family
You may qualify for a Special Enrollment Period if you or anyone in your household gained access to an Individual Coverage Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRA) or a Qualified Small Employer Health Reimbursement Arrangement in the last 60 days or expects to in the next 60 days.
Other Qualifying Changes
- Gaining membership in a federally recognized tribe
- Becoming a US citizen
- Leaving incarceration
- Starting or ending service as a AmeriCorps State and National, VISTA, or NCCC member